Identify the Stimulus for the Release of Insulin
Sener A Malaisse WJ. The fate of the beta cell when exposed to environmental triggers of the disease is determined by the possibility to adapt to the new situation by regulation of gene expression.
Handbook Of Diabetes 4th Edition Excerpt 4 Normal Physiology Of Insulin Secretion And Action
QUESTION 3 Identify the stimulus for the release of insulin.

. Insulin binds to receptors on target cells a cascade of phosphorylation leads to premade glucose channels being inserted into the membrane. For each one identify the stimulus and the response and state whether the process is positive or negative feedback. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release.
Experiments were conducted at 35 mmoll K to reveal the K ATP channelindependent pathway. In the lungs the blood gives up its oxygen OR carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen OR carbon dioxide 4. Transcribed image text.
Increased exposure to sunlight. The stimulus for insulin secretion is a HIGH blood glucoseits as simple as that. Indirectly stimulates live and skeletal muscles to store sugar.
Target cells include adipose tissue skeletal muscle and the liver. 12 Closure of K -ATP-dependent channels results in membrane depolarization and activation of voltage dependent calcium channels leading to an increase in intracellular calcium concentration. For example a rise in blood glucose levels triggers the pancreatic release of insulin.
Stimulation of glycogenesis B. For example glucose in the blood a stimulus causes the pancreas to release insulin a reaction which in turn causes the cells to take up glucose from the blood a response. The effects of thyroid hormones are more variable.
The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Solutions for Chapter 5 Problem 7OQ. Changes in the body can be mediated by direct or indirect mechanisms.
Sener A Levy J Malaisse WJ. When blood sugar rises receptors in the body sense a change. Impairment in any of the relevant processes leads to insufficient insulin release which contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes T2D.
Glucose enters through the channels. Secretion was measured in the presence of normal K concentrations 48 mmoll. Insulin secretion was measured during stimulation of INS-1derived 83213 cells 7 with 12 mmoll glucose for 4 h.
A newly discovered hormone contains four amino acids linked together. The term humoral is derived from the term humor which refers to bodily fluids such as blood. The main physiologic or pathophysiologic stimulators of glucagon release are hypoglycemia insulin-induced associated with starvation or intense muscular exercise hyperaminoacidemia the rise in plasma glucagon levels after a balanced meal is probably due mainly to amino acidinduced glucagon release stimulation of the adrenergic system stress exercise and.
In turn the control center pancreas secretes insulin into the blood effectively lowering blood sugar levels. Long term effects of K deprivation upon insulin biosynthesis and release. Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook.
If blood glucose levels decrease from normal which of the following changes takes place to bring glucose levels back to normal. It is a protein responsible for regulating blood glucose levels as part of metabolism1 The body manufactures insulin in the pancreas and the hormone is secreted by its beta cells primarily in response to glucose1 The beta cells of the pancreas are perfectly designed fuel sensors stimulated by glucose2 As glucose levels rise in the plasma of the blood uptake. Insulin is normally secreted by the beta cells a type of islet cell of the pancreas.
It is decreased by PTH. Glucose entry into the β cell is sensed by glucokinase which phosphorylates glucose to glucose-6-phosphate G6P generating ATP. This triggers pulsatile insulin secretion.
Blood pumped out of the right ventricle goes to the body OR to the lungs 3. Although there is always a low level of insulin secreted by the pancreas the amount secreted into the blood increases as the blood glucose rises. Both A and B are correct OD.
Stimulus- increase in glucose receptor- beta cells control centre- insulin sensitive cells of the hypothalamus beta cells secrete the hormone insulin. Where must the blood go before it can be sent to the entire body. Sympathetic nerve stimulation inhibits insulin release.
Model 1 - Glucose and Glucagon The control of blood sugar glucose by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. The insulin response to oral glucose is much greater than the response to intravenous glucose because an intestinal factor or factors has a powerful stimulant effect on insulin secretion. Once blood sugar levels reach homeostasis the pancreas stops releasing.
As the search for GLP-1 secretagogues would be facilitated by a better understanding of the mechanisms involved in stimulus detection and peptide release from GLP-1secreting L-cells we set out to identify key pathways used by the L-cell. A lowering of serum calcium is the stimulus for the endogenous release of adrenocortical hormone. Stimulates adipose tissue to store fat.
O A hypoglycemia B. When human tissue such as skin or a blood vessel is torn or cut the cells near the damage send out a signal that activates platelets in the vicinity. A humoral stimulus refers to the control of hormone release in response to changes in extracellular fluids such as blood or the ion concentration in the blood.
Epinephrine inhibits insulin release. Effectors- liver cells and the body cells response- decrease in blood glucose by uptake by liver cells and conversion to glycogen and uptake by body cells. Inhibition of lipogenesis O inhibition of.
Identify the chemical class under which this hormone would be classified. Neither A nor Bare correct QUESTION 4 All of the following are actions of insulin EXCEPT. The progress of this project will be the focus of this present review.
The primary stimulus for insulin secretion is A. Glucose is an effective stimulus for the release of insulin from pancreatic beta-cells but its pre-eminence for the physiological control of insulin secretion is now challenged. Can OR cannot 5.
Epinephrine norepinephrine glucagon insulin cortisol aldosterone thyroxine growth hormone estrogen and testosterone. Glucagon increases and somatostatin decreases insulin release via paracrine actions. Parathyroid hormone thyroid hormone adrenalin insulin.
Up to 10 cash back Swelling of the gel in the presence of an electrical stimulus is the main phenomenon causing insulin release while the electrophoresis of insulin molecules along the electric field also has a significant impact. Insulin release is stimulated by GH cortisol PRL and the gonadal steroids. Identify the site of release stimulus for release and the predominant action of the following hormones.
The blood be used by the cells.

5 Step Pendant Diagram Concept For Powerpoint Slidemodel Powerpoint Slide Designs Powerpoint Infographic Templates

Diabetes Type 1 And Type 2 Anatomy And Physiology I

Under Insulin Resistance Condition Adipocytes Are Not Able To Respond Download Scientific Diagram

The Science Of Emotions How It Works Psychologicalfactsschools Emotions Medical Knowledge Physics And Mathematics

Stimulus Coupling Mechanisms For Glucose Induced Insulin Secretion In Download Scientific Diagram

Insulin Release An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Simplified Scheme Of Stimulus Secretion Coupling Pathways In The Download Scientific Diagram

These Graphs Depict Schematic And Real Action Potential With Terms Including Peak Overshoot Ri Physiology Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology
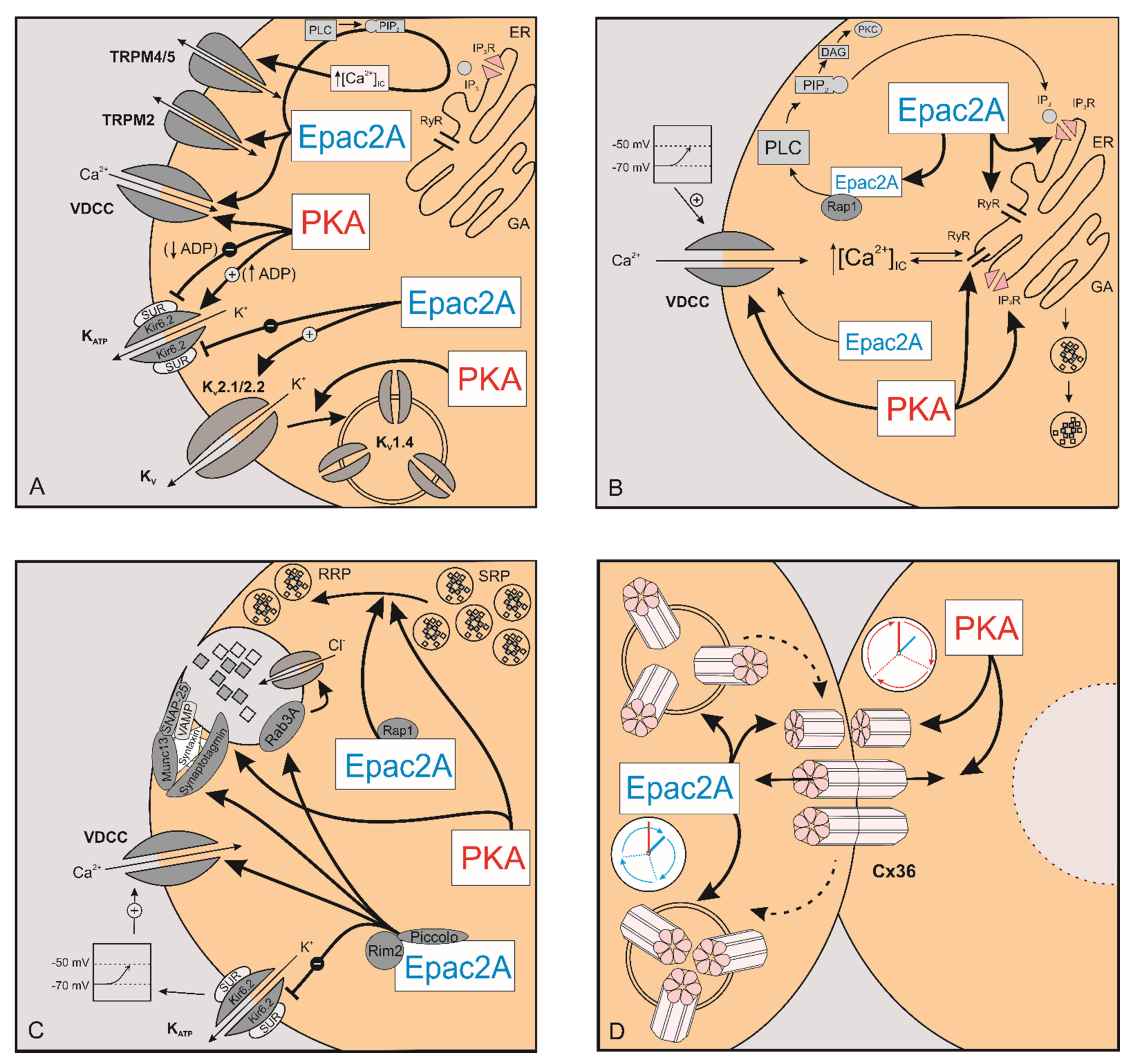
Cells Free Full Text The Role Of Camp In Beta Cell Stimulus Secretion And Intercellular Coupling Html

Stimulus Secretion Coupling In The Pancreatic Cell Glut 2 Is A Download Scientific Diagram

Homeostasis This Diagram Is Another Example Where The Body Internally Reacts And Adjusts To Out Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Physiology
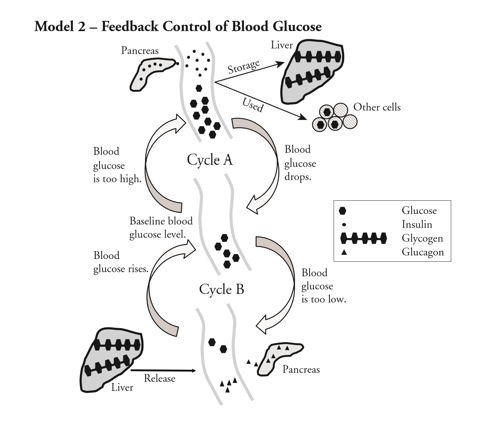
For Each Of The Letters In Model 2 Identify The Chegg Com

Stimulus Secretion Coupling An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
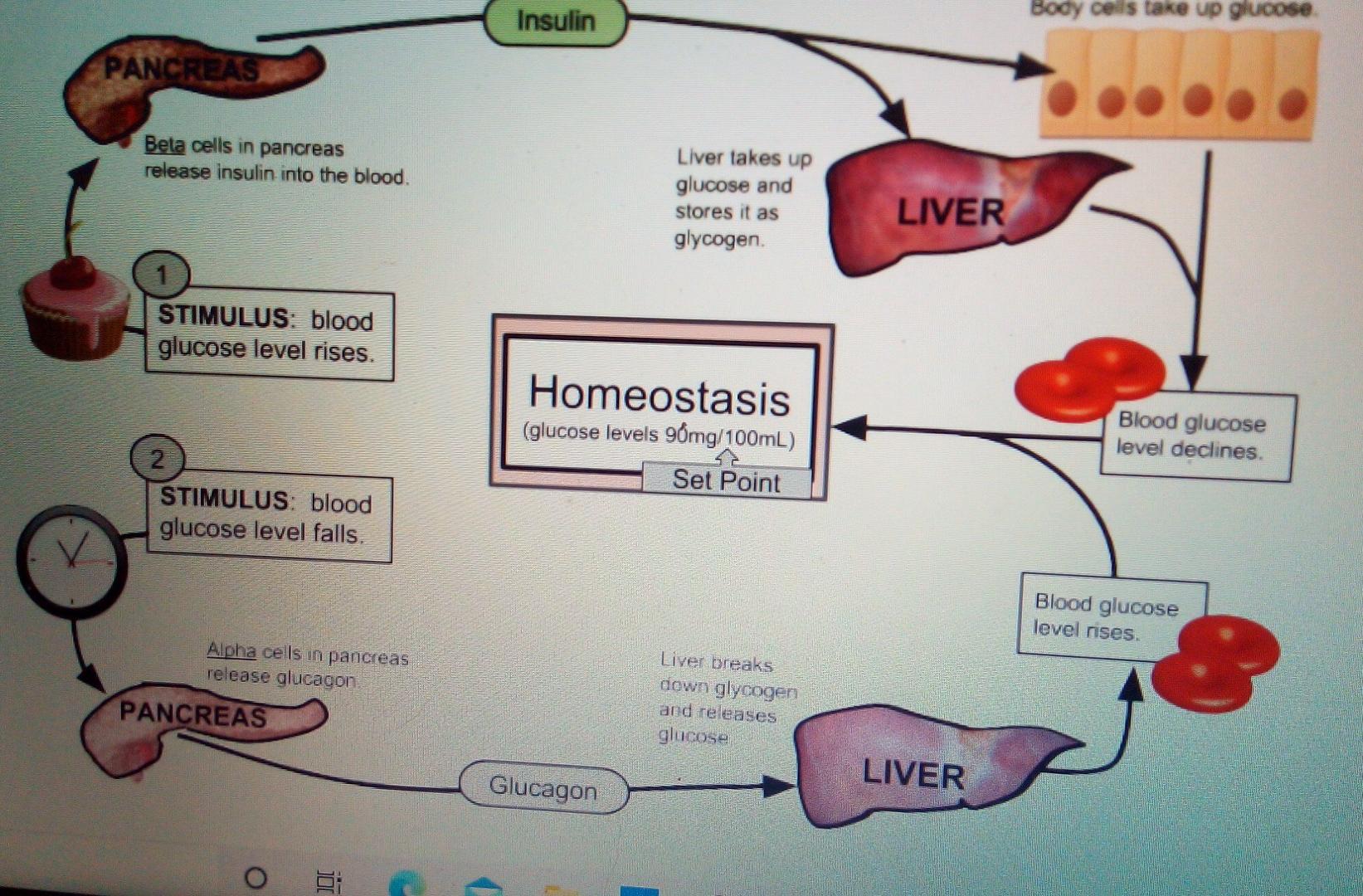
Solved Insulin Body Cells Take Up Glucose Pancreas Beta Chegg Com

Engineering Approaches In Life Science And Health Care Engineering Science Life Science Science

Stimulus Coupling Mechanisms For Glucose Induced Insulin Secretion In Download Scientific Diagram
Stimulus Secretion Coupling In The A Cell Low Glucose Concentration Download Scientific Diagram
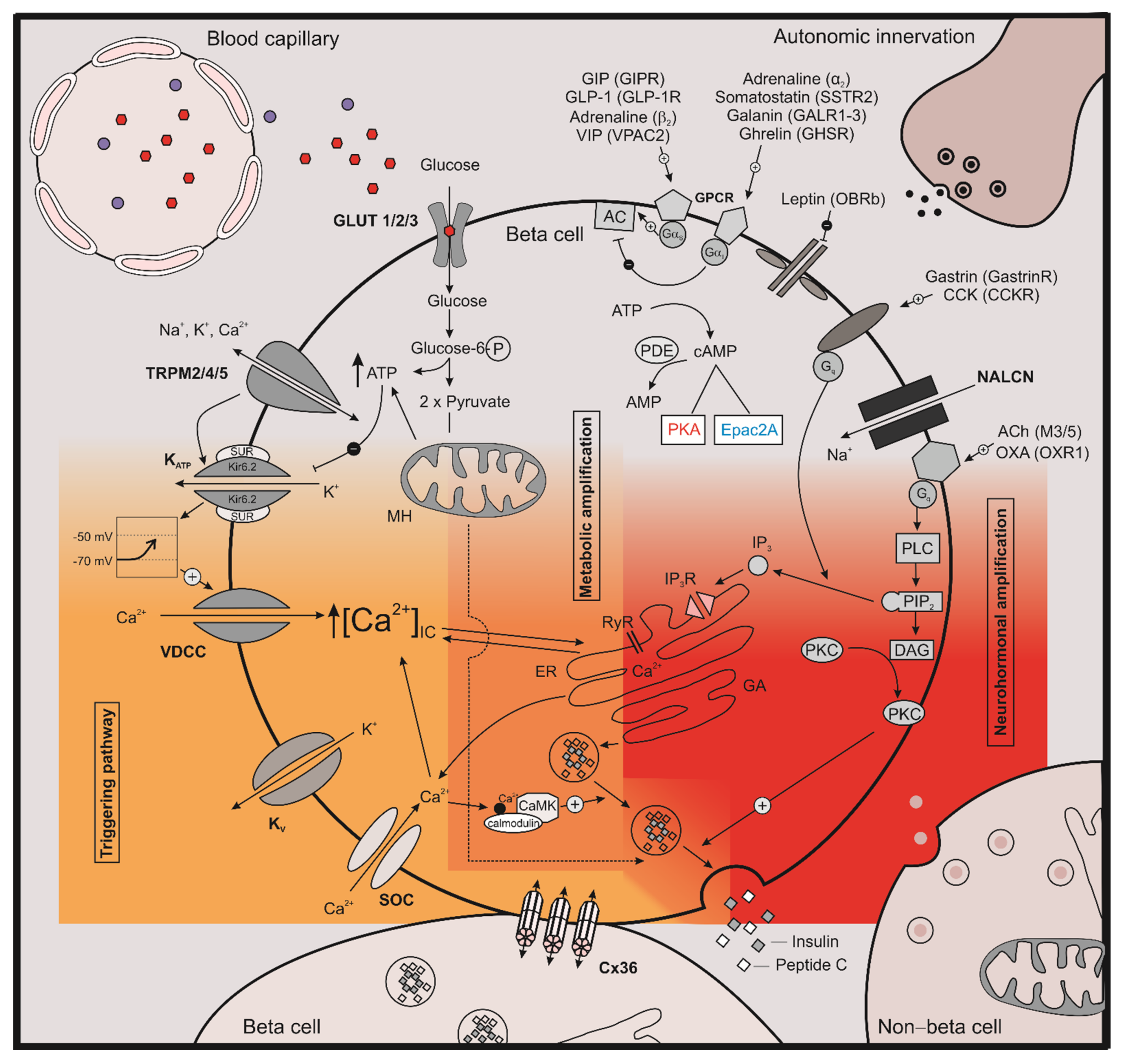
Cells Free Full Text The Role Of Camp In Beta Cell Stimulus Secretion And Intercellular Coupling Html

Glucagon Like Peptide 1 And Glucose Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Stimulate Release Of Substance P From Trpv1 And Trpa1 Expressing Sensory Nerves American Journal Of Physiology Gastrointestinal And Liver Physiology
Comments
Post a Comment